Page 53 - Implementation of ITU-T international standards for sustainable management of waste electrical and electronic equipment: The path to a circular economy in Costa Rica
P. 53
Implementation of ITU-T international standards for sustainable management of waste
electrical and electronic equipment: The path to a circular economy in Costa Rica
remaining responses mentioned one or two materials and included some materials that
do not require special treatment. However, most of them stated that they are aware of the
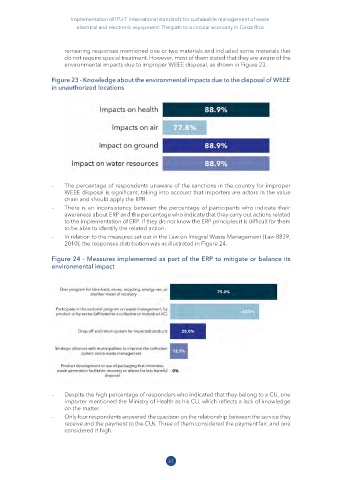
environmental impacts due to improper WEEE disposal, as shown in Figure 23.
Figure 23 - Knowledge about the environmental impacts due to the disposal of WEEE
in unauthorized locations
– The percentage of respondents unaware of the sanctions in the country for improper
WEEE disposal is significant, taking into account that importers are actors in the value
chain and should apply the EPR.
– There is an inconsistency between the percentage of participants who indicate their
awareness about ERP and the percentage who indicate that they carry out actions related
to the implementation of ERP. If they do not know the ERP principles it is difficult for them
to be able to identify the related action.
– In relation to the measures set out in the Law on Integral Waste Management (Law 8839,
2010), the responses distribution was as illustrated in Figure 24.
Figure 24 - Measures implemented as part of the ERP to mitigate or balance its
environmental impact
– Despite the high percentage of responders who indicated that they belong to a CU, one
importer mentioned the Ministry of Health as his CU, which reflects a lack of knowledge
on the matter.
– Only four respondents answered the question on the relationship between the service they
receive and the payment to the CUs. Three of them considered the payment fair, and one
considered it high.
31