Page 16 - Use cases and requirements for the vehicular multimedia networks - Focus Group on Vehicular Multimedia (FG-VM)
P. 16
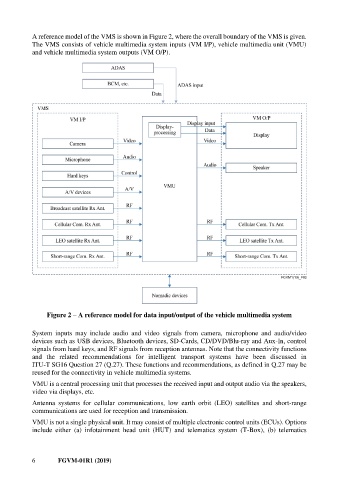
A reference model of the VMS is shown in Figure 2, where the overall boundary of the VMS is given.
The VMS consists of vehicle multimedia system inputs (VM I/P), vehicle multimedia unit (VMU)
and vehicle multimedia system outputs (VM O/P).
Figure 2 – A reference model for data input/output of the vehicle multimedia system
System inputs may include audio and video signals from camera, microphone and audio/video
devices such as USB devices, Bluetooth devices, SD-Cards, CD/DVD/Blu-ray and Aux-In, control
signals from hard keys, and RF signals from reception antennas. Note that the connectivity functions
and the related recommendations for intelligent transport systems have been discussed in
ITU-T SG16 Question 27 (Q.27). These functions and recommendations, as defined in Q.27 may be
reused for the connectivity in vehicle multimedia systems.
VMU is a central processing unit that processes the received input and output audio via the speakers,
video via displays, etc.
Antenna systems for cellular communications, low earth orbit (LEO) satellites and short-range
communications are used for reception and transmission.
VMU is not a single physical unit. It may consist of multiple electronic control units (ECUs). Options
include either (a) infotainment head unit (HUT) and telematics system (T-Box), (b) telematics
6 FGVM-01R1 (2019)