The report Greening digital companies 2023: Monitoring emissions and climate commitments, jointly authored by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the World Benchmarking Alliance (WBA), documents the emissions and energy use of 200 of the world's leading tech companies. Beyond assessing the climate data and targets of the companies, the report serves as a resource for the companies themselves to learn from best practices to improve their emissions reduction performance and accelerate the achievement of net-zero operations. Given the scale of the evaluated corporations, their climate data provide invaluable insights into the operational emissions and electricity consumption within the Information and Communications Technology sector. The annual report is now in its second edition, learn more about the 2022 edition here.
The report Greening digital companies 2023: Monitoring emissions and climate commitments, jointly authored by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the World Benchmarking Alliance (WBA), documents the emissions and energy use of 200 of the world's leading tech companies. Beyond assessing the climate data and targets of the companies, the report serves as a resource for the companies themselves to learn from best practices to improve their emissions reduction performance and accelerate the achievement of net-zero operations. Given the scale of the evaluated corporations, their climate data provide invaluable insights into the operational emissions and electricity consumption within the Information and Communications Technology sector. The annual report is now in its second edition, learn more about the 2022 edition here.
ITU and WBA organized two webinars on Greening Digital Companies on 02 October 2023 (accommodating different time zones) to launch the report.
Digital companies are playing a growing role in the race to eliminate harmful emissions from industry, transport, energy production, and other activities. By purchasing growing shares of renewable energy, investing in carbon removal, and issuing green bonds, the technology firms driving the world's digital transformation have also come to the forefront in efforts to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Learn more from the launch event and the key messages.
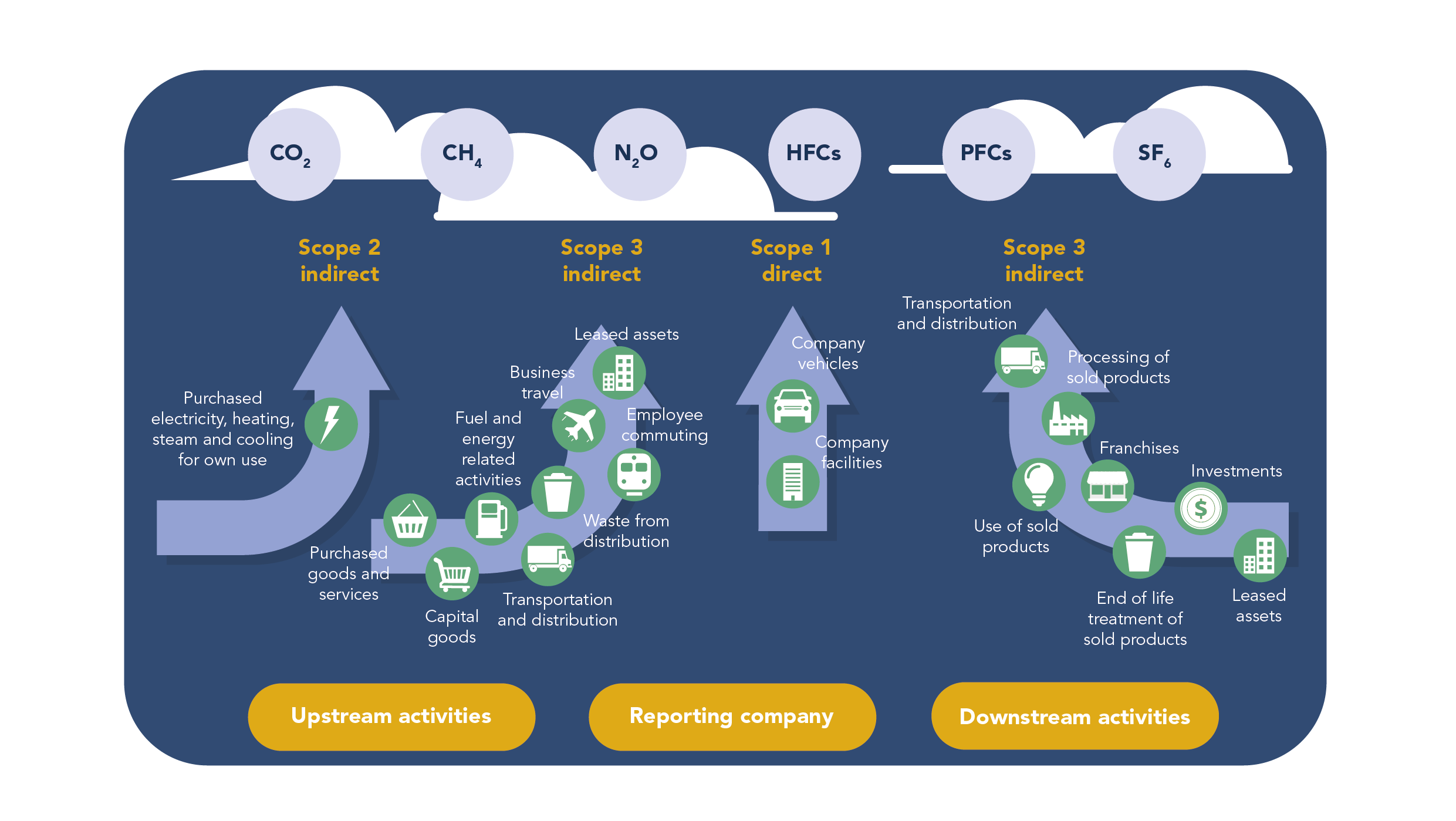
Key findings about emissions and electricity trends from digital companies:
- In 2021, 200 companies within the Digital Inclusion Benchmark (DIB) collectively emitted from operations over 260 million tCO2e, constituting 0.8 per cent of global energy-related emissions.

- The International Monetary Fund suggests that the price per tonne of carbon should be USD 75 to limit global warming. Based on this price, emissions from digital companies equates to a negative economic impact of around USD 20 billion, surpassing the GDP of half of the world's countries.
- The growth rate of GHG emissions is declining due to greener energy grids, rising electricity use, especially in data centers, presents challenges.
- Some regions, including data center hubs (Amsterdam, Dublin, Singapore), have imposed moratoriums on new data center construction due to emission and energy supply concerns.
- 4 digital companies are among the top 20 corporate consumers of electricity, the only ones outside high emitting industries (i.e., chemicals, construction, metals and mining, oil and gas, and utilities).
- Among digital companies, telecommunication service providers contribute nearly half of total operational emissions, focusing on Scope 1 and 2 location-based emissions.