
Overall, 81 countries (42 per cent of all countries worldwide) have e-waste policy, legislation, or regulation in force. However, according to June 2023 data, the growth rate of countries implementing e-waste policy, legislation, or regulations is decelerating, and most ITU Member States still have no legal instrument in place governing e-waste management. To assist Member States in balancing their economic and social development with environmental management, ITU provides a programme dedicated to e-waste policy and regulatory development.
Through previous and ongoing projects and partnerships with key players including WEF, UNEP, GIZ, CST, DITRDCA and EU Africa RISE Facility, ITU has become a trusted implementer of projects which aim to improve the national regulatory framework for e-waste management.
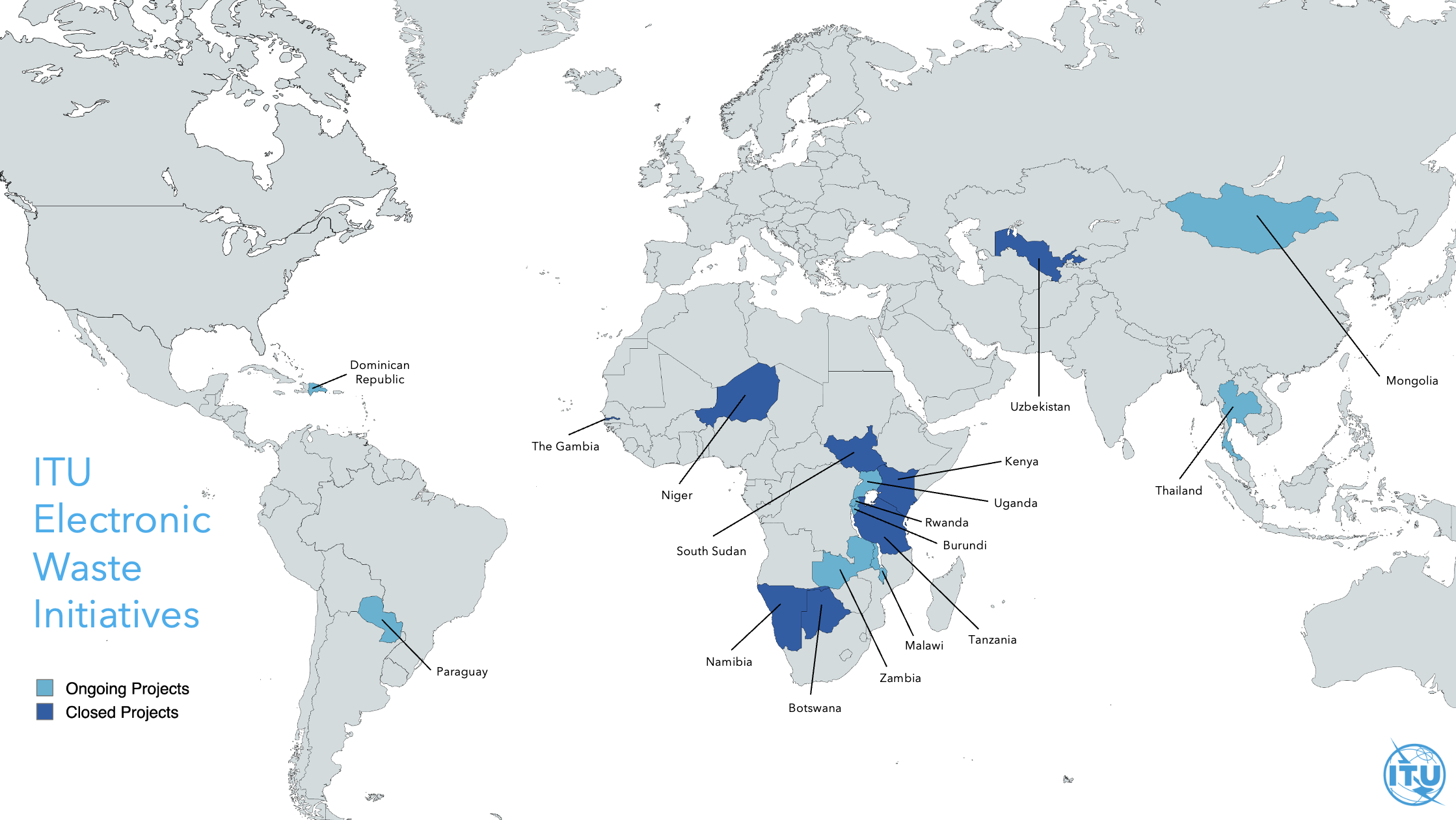
Global Impact
Having an e-waste policy or legislation in place is a significant first step for a country towards creating a system of environmentally sound e-waste management, transitioning to a circular economy for electronics and increasing the amount of e-waste collected and recycled. The Global E-waste Monitor 2024 tells us that those countries with e-waste legislation in place have on average a collection rate of 25 per cent whereas the majority of those without legislation have a collection rate close to zero.
Countries Supported