|
|
Abstracts
|
� MAIN PROGRAMME � |
|
OPENING PLENARY |
|
Keynote speech |
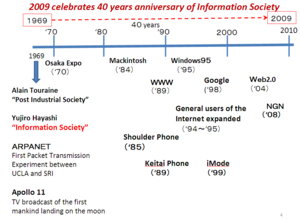
In 1969, 40 years ago, two persons
predicted the next society after
“Industrial Society”. Alain Touraine in
France predicted “Post-Industrial
Society”, and Yujiro Hayashi in Japan
described the advent of “Information
Society” after Industrial Society. In
that year, two events occurred by chance
suggesting the advent of information
society, one of which was the first
packet transmission experiment over
ARPANET between UCLA and SRI. This is
the origin of the Internet. The other
event was TV broadcast from the moon on
which the first mankind landed flying in
the Apollo No.11 Spaceship. Today we are
celebrating the 40 years anniversary of
Information Society as shown in Fig.1.
During these 40 years, ICT advanced
quite rapidly, and especially in these
ten years, the advancement of the
Internet and cellular phone networks has
been remarkable, and the economy and
daily life in the today’s society are
dependent heavily on such ICT
infrastructure. In 2010s we are going to
make progress toward “High Level of
Information Society” which will appear
in 2020s - 2030s. A new paradigm of both
computer systems and communication
networks will be envisaged as shown in
Fig. 2.
In this presentation, requirements for
the new ICT paradigm are shown, and
technological issues to realize it are
discussed.
Reference
[1] Tomonori Aoyama, “ A New Generation
Network: Beyond the Internet and NGN,”
IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol.47,
No. 5, pp.82-87, May 2009
 |
 |
|
Figure 1 - Advancement of
Information Society |
Figure 2 - New ICT Paradigm in
2020s/2030s |
|
|
Keynote presentation |
A vision of communications for the next billion
Sigurd Schuster (Nokia Siemens Networks, Germany)
Carlos Uzal (Telef�nica Latin America, Argentina)
By the end of 2008, nearly four billion
peopled used telephone and/or Internet
services on fixed and mobile networks.
We may anticipate that this number will
grow to around five billion until 2015,
with this growth coming from emerging
economies. Although there are some
growth expectations in fixed lines, the
majority of new connections is expected
to be on the mobile side.
Looking at these market projections, the
industry has to develop ways to bring
connectivity to the new users in a
highly cost effective way. At the same
time we need to have a closer look at
the services: while in many cases,
providing voice telephony to first-time
telecommunications users is already a
big step ahead, “Digital Inclusion”
needs to ensure access to the Internet
or at least Internet-like data services
as well. To implement Digital Inclusion
does only not mean to provide a personal
computer or a mobile phone with Internet
connection - this could be the first
challenge and the easiest one. Digital
inclusion is much more than that: we are
talking about reaching specific groups
of users, communities, schools, and
little remote villages, and teach them
how digital communications, services and
technology can bring benefits to their
life. In some places these challenges
seem still to be far from reality, but
we already have seen some successful
examples of innovative, Internet driven
business models providing free services
in emerging markets. Here is a big
opportunity for the telecommunications
industry. We have the ability to deploy
network access, we can team up with
partners to provide terminals, content
and knowledge to include the “next
billion” into the digital life.
On the connectivity side of
communication networks, state-of-the-art
radio technologies provide the base to
cover large areas fast and at affordable
cost. Smart site solutions for base
stations enable sustained operation in
remote locations, in many cases even
without connection to the power grid.
Tight integration with fixed
infrastructure will help to bring
backhaul cost down in populated areas.
IP based infrastructure and photonics
will help to make transport, core
networks, and basic services available
at sufficiently low cost.
On the services and applications layer,
the extended use of IT technology and a
wealth of dedicated SW applications will
help network service providers to serve
low ARPU customers, offer cheap voice
and suitable data services, and allow
for widespread usage of prepaid and
innovative payment schemes. It also
allows developing innovative business
models with new players in the value
chain and to even serve users in
locations where a traditional
telecommunications service economically
would not be feasible, or to bring
“pre-Internet” services to areas where
broadband connectivity is not
affordable.
If our industry aims at turning such a
vision into reality, this does not come
for free. Besides constructive,
cooperative work of all parties in
standardization, regulation, equipment
development, network and service
evolution and operation, we need to “go
the extra mile”: Full exploitation of
our creativity, innovation, and research
capabilities are needed - without a
close partnership between the academic
world and the industry we will fail to
meet the goal. |
|
INVITED PAPERS |
|
S1.1 |
Is digital inclusion a good thing?
How can we make sure it is?
Richard Stallman (Free Software
Foundation, USA)
Activities directed at “including” more
people in the use of digital technology
are predicated on the assumption that
such inclusion is invariably a good
thing. It appears so, when judged solely
by immediate practical convenience.
However, if we also judge in terms of
human rights, whether digital inclusion
is good or bad depends on what kind of
digital world we are to be included in.
If we wish to work towards digital
inclusion as a goal, it behooves us to
make sure it is the good kind. |
|
S1.2 |
Technology for losers: re-equipping
the excluded
Erkki Sutinen (University of Joensuu,
Finland)
The agenda of technology for losers is
closely related to a politically more
correct concept of using technology to
empower disadvantaged regions or
individuals. Technology for losers
emphasizes the fact that losers are
those that had something valuable which
they have subsequently, for whatever
reason, lost. Although commonly used as
a highly patronizing and even offensive
term, the term loser, literally, refers
to diverse users of technology such as
people marginalized because of
unemployment, individuals with special
needs, and poor people in developing
regions. Hence, together they form a
majority of the humankind. Working with
losers requires technology designers to
focus more on the urgent and urging,
concrete problems, while the traditional
perspective of disadvantaged users calls
for correct strategies at the policy
level. The key characteristic of
designing technology for losers is the
fact that it starts from the
identification of their strengths rather
than needs or lacks; thus recognizing
their ultimate resources which can be
released by re-equipping them with what
they have lost. |
|
S1.3 |
Interplay and implications of
intellectual property and
academic-industry collaboration to
foster digital inclusion
Louis Masi, Dawn Tew (IBM
Corporation)
This paper discusses how to reduce the
barriers universities and industry face
when working together on collaborative
research projects. As a best practices
study, the paper describes lessons that
should not be viewed as isolated
experiments, but as practices that can
create the synergy required to drive
collaborative research, innovation, and
digital inclusion. This is particularly
critical for developing and growth
market countries, but appropriate for
all. |
|
� TOP �
|
|
|
|
LECTURE PAPERS: Session 2 - Leveraging network-enabled services for digital inclusion |
|
S2.1 |
Towards Digital Blood-Banking
Vasileios Spyropoulos, Maria Botsivaly,
Aris Tzavaras (Technological Education
Institute of Athens, GR); Panagiotoula
Spyropoulou (General Hospital of Piraeus
“Tzaneion”, GR)
This paper constitutes a status report
of the attempts of our group during the
last decade, to contribute to the design
and the implementation of a universal
Information System with integrated
Web-Services, covering the most
important Aspects of modern Transfusion
Medicine, i.e. Medical-Managerial and
Educational issues, Clinical and
Laboratory Quality Assurance,
Hemovigilance, Financial-Managerial
topics, and finally, post Transfusion
Continuity of Care. |
|
S2.3 |
Quality of Service management for
ISP: A model and implementation
methodology based on ITU-T Rec.802
framework
Eva Ibarrola (University of the Basque
Country, ES); Jin Xiao (University of
Waterloo, CA); Fidel Liberal, Armando
Ferro (University of the Basque Country,
ES)
Quality of Service (QoS) has become one
of the most important factors among
Internet Service Providers (ISPs). The
implementation of appropriate QoS
policies is essential in order to
maintain customer loyalty and fulfill
regulators’ requirements. ITU-T
Recommendation E.802 provides a
framework for the identification of QoS
criteria relevant to the users and the
ISPs. This recommendation also provides
guidelines to derive measurable QoS
parameters from identified criteria.
This paper presents a QoS management
model and implementation methodology for
ISPs. We ground our investigation on
Rec. E.802 framework which the ISPs may
face when implementing ITU-T Rec.
G.1000. The proposed methodology is
meaningful for the users, the vendors,
and the network operators. And its
conformance to ITU-T standard makes it
suitable and deploy-ready for both
regulators and providers |
|
S2.3 |
Enhanced Advertising for Next
Generation Networks
Jose Sim�es () ; Thomas Magedanz (Fraunhofer
FOKUS, DE); Luca Lamorte, Moltchanov
Boris, Carmen Criminisi (Telecom Italia,
IT)
Telecommunication and Internet services
are constantly subject to changes,
seeking the customer’s full
satisfaction. Enriching these services
with innovative approaches such as
context-aware, mobile, adaptable and
interactive mechanisms, enables users to
experience a variety of personalized
services seamlessly across different
platforms and technologies. In this
sense, advertising is not exception,
especially if we consider that it will
become the enabler for future next
generation services. This paper,
therefore presents an architectural
approach to address advertising
solutions across different technologies
and platforms, enriching the overall
user Quality of Experience. Moreover, by
over viewing the current advertising
market scenario it provides the vision
to overcome the established advertising
paradigms focusing on key points like
user privacy protection and social
networks integration. |
|
� TOP �
|
|
|
|
LECTURE PAPERS: Session 3 - Bridging the Digital Divide for the individual |
|
S3.1 |
A model and system architecture for
ubiquitous sensor network businesses
Masugi Inoue (National Institute of
Information and Communications
Technology, JP)
We address issues concerning technology
development, environment creation, and
service model for the businesses using
ubiquitous sensor networks (USN).
Large-scale, long-term experiments with
a comprehensive system that can provide
test applications to the public under
government initiated research projects
will help us make USN businesses and
services available. Sensor cells with
the proposed managed wireless mesh
network will be able to create new USN
domains logically separated from but
cooperative with web domains on the
current Internet, providing novel,
context-aware, interactive services to
users with the use of information from
sensors deployed across heterogeneous
networks. We also present USN business
platform composed of communications,
information management, and application
platforms as a big picture of our idea
about system architecture. A milestone
on the road toward realizing USN
businesses is also introduced. |
|
S3.2 |
Discrimination in NGN service
markets: Opportunity or barrier to
digital inclusion?
Fernando Beltran (University of
Auckland, NZ); Lina Gomez (Centro de
Investigacion de las Telecomunicaciones,
CO)
The promise of digital inclusion may be
deterred by different sorts of
discrimination brought about by
Next-Generation Network (NGN) operators.
As the growth of fixed and mobile
networks relies on private investment
and sufficient regulatory and economic
incentives, competition in different
telecommunications markets will
increasingly depend on providers’
ability to differentiate their product
and discriminate among consumers. Unless
the industry – operators, content
providers, regulatory and competition
authorities – fully understands and
exploits the welfare enhancing role of
discrimination in the new environment,
NGN’s promises of universal and
ubiquitous access, sustainability and
affordability might be only incipiently
achieved. |
|
S3.3 |
Global effort on Bridging the Digital
Divide and the role of ICT
standardization
Mario Canazza (National
Telecommunications Agency, BR)
In the year 2000, at the dawn of the
21st century, World Leaders from 189
States gathered at the United Nations
(UN) Millennium Summit to discuss the
Millennium Development Goals. In order
to achieve the goal of eradicating
poverty by the year 2015, one of the
resolves of the UN Millennium
Declaration was to ensure that the
benefits of Information and
Communication Technologies (ICTs) are
available to all. A digital divide
between developed and developing
countries was identified, a global
effort to bridge this divide was set
forth, but what has the world
effectively accomplished upon this goal?
How do new concepts such as the Internet
economy and digital convergence relate
to the task of bridging the digital
divide? What is the role of ICT
standardization in bridging the digital
divide? This paper will shed some light
on these issues. |
|
S3.4 |
Universal Digital Inclusion: Beyond
Connectivity, Affordability and
Capability
Mamello Thinyane (University of Fort
Hare, ZA); Alfredo Terzoli (Rhodes
University, ZA)
Traditionally digital marginalization
and exclusion were understood to be a
factor of connectivity to the Internet,
affordability of the technology, and the
capability of the communities to utilize
the technology. ICT for development
(ICT4D) interventions have been
undertaken that address these specific
factors of marginalization, however, it
remains that communities are still
excluded from the global knowledge
society. In this paper we argue that key
factors towards reaching greater
inclusion and participation of the
digitally marginalized communinities,
are the knowledge-centricity and
context-sensitivity of the undertaken
interventions. The solutions developed,
and the services deployed, must
intrinsically encapsulate the local
knowledge within the community of
deployment. Based on this premise we
have developed an architectural
framework, named PIASK, that formalizes
the contextualization of the developed
applications within the socio-technical
environment and positions them within
the local knowledge system of the
community. We highlight the components
of this architecture and discuss its
implementation through a knowledge
platform for a community in South
Africa. |
|
� TOP �
|
|
|
|
LECTURE PAPERS: Session 4 - Network architectures today and tomorrow |
|
S4.1 |
RoFSO: A universal platform for
convergence of fiber and free-space
optical communication networks
Kamugisha Kazaura, Kazuhiko Wakamori,
Mitsuji Matsumoto (Waseda University,
JP); Takeshi Higashino, Katsutoshi
Tsukamoto, Shozo Komaki (Osaka
University, JP)
The demand on capacity and quality
offered over wireless communication
links has pushed researchers to innovate
new design methodologies and concepts
over wireless systems and networks with
the ultimate aim towards achieving a
Next Generation Network (NGN). Among the
emerging technologies is the Radio on
Free Space Optics (RoFSO) system
described in this paper. With this
technology it is possible to
simultaneously transmit multiple RF
signals comprised of various wireless
services over FSO links using WDM
technology. The technology can be
applied as a universal platform for
providing convergence of fiber and
free-space optical communication
networks extending broadband
connectivity to underserved areas. We
present the design concept and highlight
some experimental results obtained from
performance evaluation of the RoFSO
system we have developed. The results
demonstrate a satisfactory performance
in terms of reliability and stability
based on the quality metric parameters
defined for the different RF services
signals transmitted over the RoFSO
system. Considering the potential of the
RoFSO technology we propose a study for
standardization work in the ITU as an
initiative which can lead to its rapid
adaptation. |
|
S4.2 |
An ID/Locator Split Architecture of
Future Networks
Ved Kafle, Hideki Otsuki, Masugi Inoue
(National Institute of Information and
Communications Technology, JP)
The ID/locator split concept has
recently been introduced into the ITU-T
Study Group 13’s standardization
activities for future networks. To
contribute to ITU-T’s this effort, we
first propose a naming system and then
present a new ID/locator split
architecture based on the naming system.
The proposed architecture uses distinct
sets of values for host identifiers and
locators, thus allowing the network
layer protocols to change locators
without requiring the upper layers to
change identifiers. This capability is
helpful for designing efficient
solutions to mobility and multihoming. |
|
S4.3 |
Mobile-NGN Architecture based on REST
concept
Yoshitoshi Murata (Iwate Prefectural
University, JP)
A new Mobile-NGN architecture based on
the REST (representational state
transfer) concept is proposed. A mobile
communication service is established by
combining divided network resources such
as Web services derived from REST
technology in this architecture. Mobile
terminals will be able to use Web
services, including telephone service,
via just a web browser and plug-in
programs. This architecture overcomes
the problems of the open heterogeneous
mobile network (OHMN), which despite
being based the horizontal divided
business model, lets a business player
who provides the call session control
function (CSCF) easily control the
mobile communication market. Our
architecture will make it easy for new
access network provides (ANPs) to enter
the wireless communication market, which
will accelerate competition among
players, leading to the development of
innovative new applications. |
|
S4.3 |
Reliability and Scalability Analysis
of Low Cost Long Distance IP-Based
Wireless Networks
Riccardo Stefanelli, Alessandro
Galardini (iXem Labs, Politecnico di
Torino, IT); Daniele Trinchero (Politecnico
di Torino, IT)
Low cost digital radios are sometimes
proposed as an affordable tool for the
realization of long distance (multikilometric
- MKM) point-to-point telecommunication
infrastructures in Developing Countries.
To analyze the performance and the
reliability of an architecture based on
use of cheap wireless cards, several
point-to-point links ranging from 50 up
to 300 kilometers have been implemented
in harsh environments. The links make
use of commercial IEEE802.11a/h radios.
For the purpose of the research, some
modifications to the PHY and MAC layers
of the standard 802.11 protocol have
been implemented. Data rate enhancements
have been obtained combining and
transmitting several channels through
the same antenna. Performance and
stability have been monitored,
continuously, for about 18 months.
Reliability and scalability have been
analyzed, taking into account the
complexity of different kinds of
scenarios. Interesting results have been
reported, showing that, thanks to its
inexpensive features, this technological
solution may be used as a starting
process to realize backhaul links and
transport wideband connectivity in poor
and isolated regions. |
|
� TOP �
|
|
|
|
LECTURE PAPERS: Session 5 - Broadband for everyone |
|
S5.1 |
Innovative broadband models
for digital inclusion
Supavadee Aramvith (Chulalongkorn University, TH), Prasit Prapinmongkolkarn, Akarapon Kongchanagul (National Telecommunications Commission, TH) Ekachai Phakdurong, Udomsak Luengkhwan, Chatpetch Bunyakate (Thaicom PLC, TH)
In order to provide equal
telecommunications access to villages,
schools and health centers in remote
areas, various innovative broadband
models have recently been developed
jointly by operators and Thailand’s
National Telecommunications Commission (NTC),
using the capacity demand sharing
IP-based broadband communication
technique. This paper presents and
compares three innovative broadband
models, namely, IP broadband satellite,
WiMAX and CDMA 470. Various novel
concepts in systems deployment and
development of ground equipment
technology enabling a more efficient use
of spectrum are presented. |
|
S5.2 |
Dynamic Resource Management for
Downlink Multimedia Traffic in OFDMA
Cellular Networks
Dhananjay Kumar, Chellappan Chellappan,
Srividhya Subramanian, Mariappan Pandian,
Martheeswaran Mohandoss (Anna
University, IN)
Because of bursty high data rate and
delay sensitive nature of high quality
multimedia application, the resource
allocation in wireless network to meet
its quality of service (QoS) has become
the most challenging and interesting
issue. Orthogonal Frequency Division
Multiple Access (OFDMA) employing
adaptive channel allocation technique
can support these requirement while
increasing the system capacity many
fold. Here, an efficient resource
allocation method called Two Stage Rate
Adaptive (TSRA) algorithm is proposed in
order to meet dynamic bandwidth
requirement in downlink. We model the
resource allocation problem with goal of
maximizing spectral efficiency.
Considering random mix of four
categories of multimedia traffic, we
find that gap between analytical and
simulated average capacity of the system
gets smaller as number of user increases
and at one point the simulated average
system capacity exceeds 6 b/s per Hz.
Further, other system parameters like
average throughput, delay and BER of the
TSRA protocol is presented. |
|
S5.3 |
Optical Transport Networks: from
all-optical to digital
Virgilio Puglia (IT); Olga Zadedyurina
(University of Trento, IT)
This work gives an overview of optical
transport networks evolution. Namely it
describes the tendency of shifting from
all-optical to digital transport
networks concept. Within this context we
consider two main technologies IPoDWDM
and optical digital network as new
solutions that replace the classical
all-optical transport network model.
Possible integration of different
approaches is proposed. |
|
� TOP �
|
|
|
|
LECTURE PAPERS: Session 6 - Open and accessible services for digital inclusion |
|
S6.1 |
iCanSee: A SIM Based Application for
Digital Inclusion of the Visually
Impaired Community
Hannah Thinyane (Rhodes University, ZA);
Mamello Thinyane (University of Fort
Hare, ZA)
The digital divide is a term often used
to describe differences between rich and
poor communities. This term however is
more encompassing than that, as it
relates to the divide between those who
have access to information and
communication technologies (ICTs) and
those who don’t. Due to the small screen
size, and resulting small font size and
low contrast supported by most mobile
phones, the visually impaired community
fall into this category of having little
access to this popular ICT. This paper
presents iCanSee, a SIM based
application built on a Smart Card Web
Server (SCWS), developed particularly
for the visually impaired community. It
provides a web-based front end to the
four most frequently used text-based
communication tools on a mobile phone:
the phone book; SMS; MMS; and email.
iCanSee allows users to create their own
CSS profiles, supporting changes to:
background and font colour (for
contrast); and font size. As the CSS
file is stored on the SIM rather than
the handset itself, when the user
upgrades to a new mobile handset, all
their settings are transferred along
with other personal information such as
their address book. |
|
S6.2 |
An asterisk-based framework for
e-learning using open protocols and open
source software
Mosiuoa Tsietsi, Zelalem Shibeshi,
Alfredo Terzoli, George Wells (Rhodes
University, ZA)
This paper describes the conceptual
design of an e-learning system that is
based on open protocols and open source
software. This is an initial step
towards providing a framework within
which remote lectures at our university
can be conducted with other institutions
in the Southern African region, both
those that we currently have learning
programs with, and those that will be
forged in the future. The motivation for
this effort is born out of a desire to
avoid expensive and inflexible
commercial tools that have been used in
the past, with often undesirable
effects. Our design promises to deliver
most of the features that can be
expected of a modern e-learning system
such as a web interface, a space for
lecture material, real-time audio and
video support, instant messaging and the
ability to convey presence. We have also
identified two modes of operation, one
as a web-based video archive and another
as a live virtual classroom. It is hoped
that this dual-mode setup will support
different modes of learning for students
and suit varying bandwidth restrictions
among institutions. |
|
S6.3 |
Innovations for Digital Inclusion:
Leveraging Next Generation Networks for
Human Development from the Bottom of the
Pyramid
Walter Brown (Monash South Africa, ZA)
Global migration to Next Generation
Networks (NGN) is progressing rapidly,
driven by competition, declining
revenues from traditional ICT networks,
new service opportunities and cost
reductions from underlying technological
advances. If history follows its normal
course, 72% of the world’s population
will be excluded from the full benefits
of this migration. This paper examines
the possibility of leverage South
Africa’s migration to NGNs for the
development of unique ICT support
networks and services for human
development at the base of the country’s
development pyramid (BOP). A bottom-up
research strategy aimed at complementing
traditional top-down human and ICT
development strategies to reverse the
growing levels of digital exclusion is
proposed. |
|
� TOP �
|
|
|
|
LECTURE PAPERS: Session 7 - Public policies, standards and digital inclusion |
|
S7.1 |
Government Role in Information and
Communications Technology Innovations
Mostafa Hashem Sherif (AT&T, US);
DongBack Seo (University of Groningen,
NL)
In this paper we analyze Government’s
role in various types of information and
communications technology (ICT). In the
current global financial crisis, the
question is no longer about whether a
government should be involved in an
industry, but when and how it should
intervene. We propose a framework
analysis to guide public policy by
combining changes in technology and in
the value chain. We show how to use that
framework to understand how various
governments have intervened in
industrial development, including
standardization, and how their roles
have impacted the related industries. |
|
S7.2 |
New model for cost of equity
evaluation in emerging markets: the
telecommunication sector in Brazil
Tullio Bertini (National
Telecommunications Agency, BR)
This paper proposes a new model for
evaluating cost of capital in emerging
markets. This model stands out by an
index that weights country risk premium,
on the assumption that emerging markets
are partially integrated and where
investors from those markets have a
globally diversified portfolio. The
index created under the proposed new
model for evaluating cost of capital
seeks to capture the potential of each
asset to the risk diversification of a
global market’s portfolio. The index is
calculated using shares of
telecommunication sectors of Brazil. The
results show that the index created
(Pod) to compose the model is consistent
with the potential of each asset of the
telecommunications sector to diversify
risks of a global portfolio. |
|
S7.3 |
ICT Standardization in China, the EU,
and the US
Kai Jakobs (RWTH Aachen University, DE)
The paper looks at the ongoing efforts
in the area of standardisation of ICT
systems from a European perspective. It
briefly introduces the major players in
the field in the EU, China, and the US.
It then looks at various aspects of the
respective standardisation processes,
and identifies similarities and
differences. A brief SWOT analysis is
also provided. |
|
� TOP �
|
|
|
|
POSTER PAPERS: Showcasing Digital Inclusion opportunities |
|
P.1 |
Lower the Frequency to Trigger
Digital Inclusion? A Comparative Study
Among Different VHF/UHF/SHF Solutions for
the Implementation of Broadband Wireless
Access
Daniele Trinchero (Politecnico
di Torino, IT); Riccardo Stefanelli,
Federico Longobardi, Alessandro
Galardini, Benedetta Fiorelli (iXem
Labs, Politecnico di Torino, IT)
In the last decades the most
advantageous opportunity to improve data
rate and transport capacity over
wireless connections has been made
available by a progressive upper-shift
of the frequency of the carrier. As a
matter of fact, increasing the carrier
frequency, channel allocation and
modulation bandwidth can be increased.
Unfortunately, in parallel, path losses
augment, and obstacles, humidity and
weather affect more negatively
radio-transmissions. To face propagation
losses, the number of installations is
increased and the service area reduced,
allowing the frequency reuse, but
generating also an exponential raise of
hardware costs. As a consequence, this
strategy is unsuitable in Developing
Countries. Inverting the trend, this
paper presents a study carried out by
means of several simulations, to
evaluate coverage opportunities and cost
impact by reducing the radiofrequency
carrier, without varying any base-band
characteristic of the communication
platform. To this purpose, as an
application example, low cost IP-based
wireless cards implementing OFDM
modulation were considered, at
progressively lower frequencies, from
5.5 GHz down to 180 MHz. The comparison
was run in real contexts, and applied to
the region of El Carmen, Guayas, in
Ecuador and the region, of Antsirabe
Rural, Antananarivo, in Madagascar. In
the first one, a proper network will be
implemented by the end of 2009, in the
framework of the “Innovation for
Development Program” of the
InterAmerican Development Bank. |
|
P.2 |
On the relevance of Open Wireless
Sensors for NGN
Marco Zennaro (KTH,
IT); Herve' Ntareme (KTH, SE); Antoine
Bagula, Gordon Inggs, Simon Scott
(University of Cape Town, ZA)
Open Wireless Sensors are based on the Open Source Software and Open Source Hardware paradigms. The code used to program them and the information about the hardware design are freely released. We present the main characteristics of Open Wireless Sensor Networks (OWSNs) and report on two examples with the experimental results revealing the performance of OWSNs in terms of link quality and battery life. We demonstrate the relevance of using OWSNs in Next Generation Networks by showing the advantages of the Open Source model when applied to Wireless Sensor networks in terms of cost, personalisation and independence from a single entity as compared to proprietary solutions. |
|
P.3 |
Techno-Economical Comparison Between
Gpon And Epon Networks
Mauricio
L�pez Bonilla, Felipe Rudge Barbosa,
Edson Moschim (State University of
Campinas, BR)
Taking in consideration two leading high
capacity optical access technologies,
this paper presents a simple cost
comparison between GPON and EPON
platforms, exposing their major
characteristics, making a comparative
analysis to find the advantages and
disadvantages between these two
technologies. The work includes studies
on the economic and technical
feasibility of implementing a passive
optical network; and the choice of valid
economic and technical arguments at the
moments of planning, establishing or
expanding these networks in a given
region. The techno-economic balance
today clearly points to GPON technology,
despite the high volume of IP-Ethernet
data traffic which favours EPON. |
|
P.4 |
A demonstrative link design of RoFSO
and its Optimum performance - Indoor
short range experiment and a new model
of optical scintillation
Takeshi
Higashino, Katsutoshi Tsukamoto, Shozo
Komaki (Osaka University, JP); Kamugisha
Kazaura, Kazuhiko Wakamori, Mitsuji
Matsumoto (Waseda University, JP)
We have been developing a new type of
DWDM Radio on Free Space Optics (RoFSO)
system to transmit four radio services
on a point-to-point optical wireless
link, which can provide on universal
platform for heterogeneous broadband
wireless access in especially rural area
with no fiber infrastructure. The
developed RoFSO transceiver can directly
transmit multiple radio-on-fiber signals
from an optical fiber to air, and can
receive an optical signal from air into
a fiber core. The paper will first
present transmission qualities of 3G
cellular (W-CDMA), WiFi (11g and 11a),
and terrestrial digital television
broadcasting (DTV). Next, demonstrative
optimal RoFSO link design in terms of
power and noise budget for optical link
loss to satisfy the radio regulations
based on the measured data. The optimal
optical power allocation among 4 DWDM
channels for four radio services under
the power limitation of eye safety
regulation will be presented. |
|
P.5 |
Strategies for using international
domain standards within a national
context: the case of the Dutch temporary
staffing industry
Erwin Folmer
(University of Twente, NL); Jack
Verhoosel, Michael van Bekkum (TNO-ICT,
NL)
This paper will discuss strategies for
using international domain standards
within a national context. The various
strategies are illustrated by means of a
case study of the temporary staffing
industry. |
|
P.6 |
Application of emerging wireless
technologies for videoconference and
telehealth in rural migrant comunities
in Oaxaca, Mexico
Arturo Serrano Santoyo, Alvaro Armenta (CICESE,
MX)
The state of Oaxaca is a major sending
of migrants who make their way to Baja
California (San Quintin) in Mexico and
San Diego County (mainly to the area of
Vista) in the United States. The
intensity of migration flows from Oaxaca
to both Baja California and San Diego
County makes the area an attractive case
to apply information and communications
technologies (ICT) and public policy
strategies to explore applications of
mobile videoconferencing technology that
have socio-economic impact for migrants
and their families in Oaxaca. This
article describes a collaborative effort
of CICESE Research Center in Ensenada
Mexico, the Center for Research and
Education in Economics, CIDE in Mexico
City and the Center for Mexico-US
Studies of the University of California
in San Diego. We believe that working
together for a common goal of prosperity
for the people of both countries using
ICT’s has an important social
contribution. |
|
P.7 |
Digital Inclusion and Cyberart: the
case of the project PROEJA Transiarte
Tube
Lucio Teles, Aline Zim
(University of Bras�lia, BR)
In this paper we discuss the activities
of a group of PROEJA students
(Integrated Professional Education and
the Education of Young and Adults) about
digital inclusion, creativity, and
recovery of cultural identity as
producers of cyberart. The concept of "transiarte"
was developed as the art of transition
between the virtual spaces (cyberart)
and the real spaces (popular art). This
is a project funded by CAPES / SETEC,
called PROEJA-Transiarte, formed by the
partnership among the University of
Bras�lia (UnB), the Federal University
of Goi�s (UFG), Federal Center of
Technological Education of Goi�s (GO-CEFET)
and Catholic University of Goi�s (UCG).
The concept of creativity in cyberart is
understood in a broad sense, because
there is no consensus on the issue. The
cultural identity also happens in a
broad context, where the members of the
group define their parameters. Some
productions are discussed from the
collective and individual creation that
moves from the physical to virtual art.
In the context of educational research,
transiarte is understood as a mean of
digital inclusion, which, besides
enabling the use of Information
Communication Technologies (ICT), can
rescue the cultural identity and promote
the creativity of participants. |
|
P.8 |
A Design of XML Schema for
Information Presentation System using
Augmented Reality in New Generation
Network Management
Kei Wada,
Yoshihiro Kawahara, Tohru Asami (The
University of Tokyo, JP)
In coming ubiquitous network society, a
user who has no knowledge about network
technology might have to manage his/her
network including information appliances
and sensor networks. Current network is,
however, too difficult to manage,
because protocols to access ubiquitous
network devices are not same and it is
not easy to identify the cause of
problems if a network failure occurs.
Toward uniting protocols to access
devices, we have designed Tambourine
framework, which uses REST API to hide
SNMP, NETCONF and proprietary protocols
for sensor networks and enables users to
manage devices using HTTP and XML.
However, Tambourine framework does not
have an information presentation system
which provides users with information
without understanding of the network
configuration. To bind real devices with
the logical network configuration, we
focus on Augmented Reality (AR)
technology and designed an information
presentation system using AR technology,
which enables users to monitor the
device information displayed on that
device. The object overlaid on AR is
configured by XML file. XML has broad
utilities, and our system provides users
with an information presentation which
meets their requirement. Furthermore,
our system has user identification
system and flexible information
presentation system which changes CG
objects according to the user’s request. |
|
P.9 |
Feasibility study and implementation
by means of a pilot plan of a system of
transmission of medical images for the
diagnosis of patients between general
doctors and medical specialists
Juan Bernal, Karen Espitia (Universidad
Distrital Francisco Jose de Caldas, CO)
At the moment, in the different clinics
and hospitals of the country, there is a
trend toward the reduction of costs and
optimization of resources obeying to the
new tendencies of hospitable
administration, for such reason it is
not possible to have specialist doctors
in each hospital or center of health.
This project suggests a solution through
a technological route to a real problem.
This technological solution is a system
that allows a general doctor to take the
pertinent examinations to the patient
and to send them to the specialist
doctor so that he interprets this and he
can give his support to the general
doctor of very fast and efficient way.
For the analysis of patients is
suggested to send diagnostic images
through a transmission network using
UMTS technology. UMTS has an excellent
transmission speed and most importantly,
the network already exists, with good
coverage, which reduces costs. Using a
GSM wireless modem, this serves as an
interface between the network and the
PC, and using software management. |
|
P.10 |
Policy-based Charging and High
Precision Control for Converged
Multi-gigabit IP Networks
Taesang
Choi, Sangsik Yoon, Sangwan Kim, Dongwon Kang, Joonkyung Lee (Electronic and Telecommunications
Research Institute, KR)
Traditionally, charging in IP
networks was managed in a simple manner
such as flat-rate charging in fixed
environment or packet/byte based
charging in mobile environment. This is
mainly due to the fact that precise
traffic metering in a high-speed IP
network environment was not a simple
task. Control of such traffic was
another big challenge. This paper
addresses such complicated issues and
proposes a noble solution which can
precisely meter traffic in a high-speed
IP networks, classify them per
applications, create charging
information, and control per application
basis if necessary. It includes
requirements, architecture, and
mechanisms in a standardized manner. |
|
P.11 |
Digital Inclusion through Localism
Paul Plantinga (Monash University, ZA)
The evolution to a global
information society will require the
federation of innumerable technologies
and social systems. The resulting
increase in flexibility, diversity, and
complexity is both an opportunity and
challenge for ICT practitioners to shape
this evolution for the benefit of
developing countries and marginalised
communities. A conceptual framework is
developed to describe the weaknesses of
a centralised, top-down approach to ICT
development in being able to leverage
flexibility and manage complexity
towards a more inclusive information
society. We extend the framework by
proposing an alternative approach based
on a pragmatic form of localism,
involving decentralised participation
with national and global linkages.
Following an application of the
framework in a case study on a
developing country’s ICT development, we
use it to argue for the adoption of
localism principles in the ongoing
development of the Next Generation
Network (NGN). |
|
P.12 |
Digital inclusion opportunities in
the telecommunications sector through
NGN and Open Source tools: the Open IMS
core experience
Alberto Diez
Albaladejo, Peter Weik, Dragos Vingarzan,
Thomas Magedanz (Fraunhofer FOKUS, DE)
The evolution of telecommunication
networks towards a NGN may positively
impact the transformation of the digital
divide, a symptom of the differences in
economic and social development between
countries, into a digital opportunity.
With regard to the telecommunication
sector, the NGN evolution with its
standardization process and the
establishment of open APIs provides a
more accessible framework for
technological innovation, also for
developing economies. Learning from
previous experiences of development
projects, this article analyzes the
opportunities for the telecommunication
community to contribute to the reduction
of the digital divide. It also presents
the experience of the authors by easing
the adoption of NGN technologies through
an Open Source project. |
|
� TOP �
|
|
� MAIN PROGRAMME � |
|
|
|
|
|



